Steel for general construction
Steel for general construction
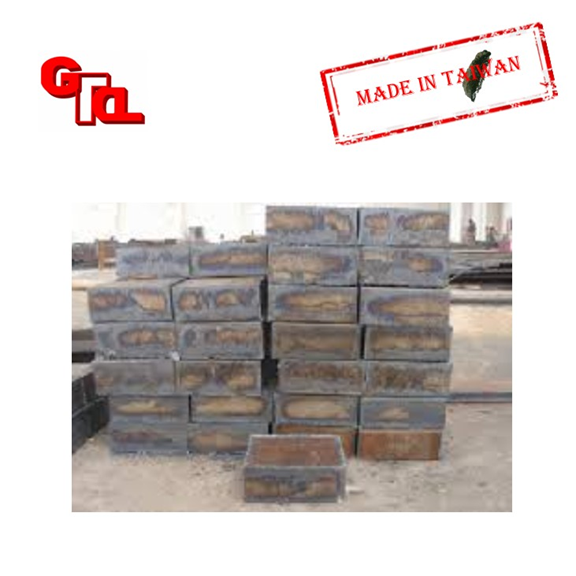
SS400

Features
SS400 (new) S gauge steel, S gauge structural steel, 400 gauge, no less than 400N/mm2 (SS41 (old) S gauge steel, S gauge construction steel, 41 gauge, tensile strength not less than 41Kg/mm2).
Uses
Rolled steels for general structures include SS41 and SS50, which are cheap and easy to obtain, but are soft and have pinholes, so they are often used for parts with low strength and hardness requirements.
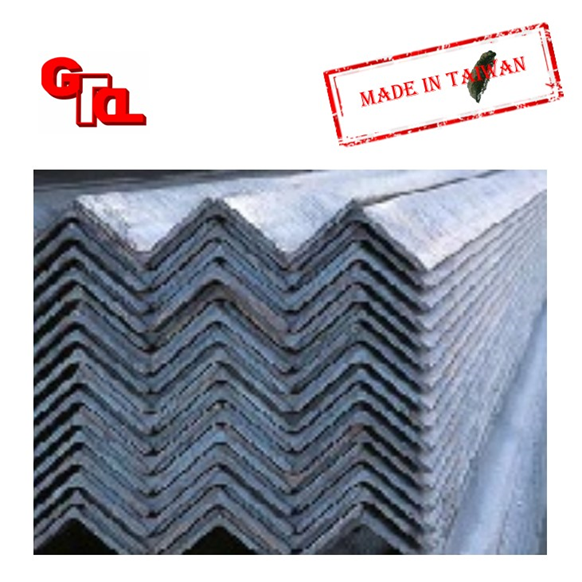
Angle Steel

Features
Angle steel, commonly known as angle iron, is a long strip of steel whose two sides are perpendicular to each other. There are equilateral angles and unequal angles. The two sides of equilateral angle steel are equal in width. The specifications of angle irons are expressed in characteristic millimeters of side width × side width × side thickness. (Equal and Unequal Angles)
Uses
It can be used to compose various stress-bearing components according to the different needs of the structure, and can also be used as a connection between components. It is widely used in various building structures and engineering structures, such as house beams, bridges, and uses: power transmission towers, lifting and transporting machinery, ships, industrial furnaces, reaction towers, container racks and warehouse shelves.
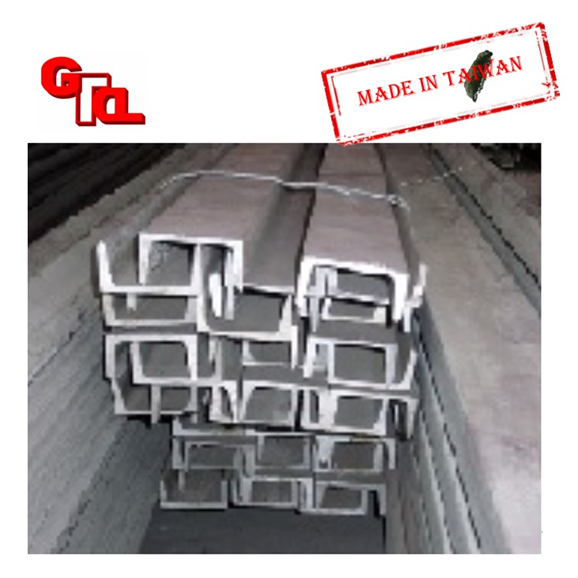
Channel iron

Features
Channel iron is divided into ordinary channel iron and light channel iron. Channel steel is often used in conjunction with H-shaped steel. (Channel)
Uses
According to the theory of steel structure, the channel steel wing plate should be stressed, that is, the channel steel should stand up, not lying down. Channel iron is mainly used for load-bearing structures such as building structures, plant structures, bridges, and mechanical assembly, as well as general structures.
I-beam
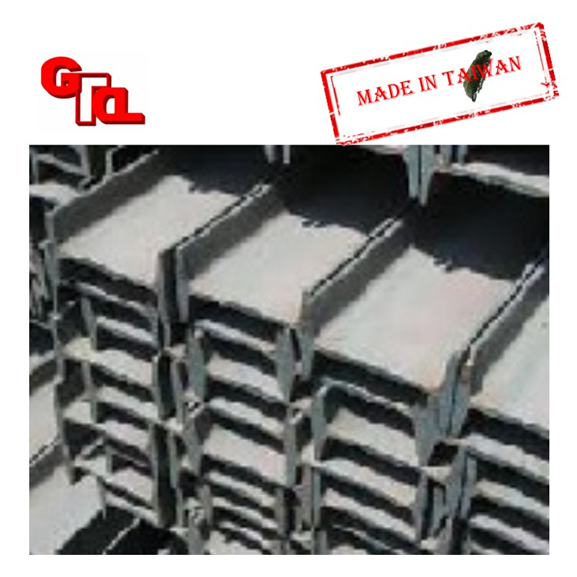
Features
I-beam and H-beam are different in the thickness of the wing plate (inclined foot), the thickness of the flange of the H-beam is the same, and the flange thickness of the I-beam is oblique and sloped It is 1:6. (Type I features: steel I-Beam)
Uses
Widely used in various building structures and engineering structures, such as building beams, bridges, power transmission towers, lifting and transporting machinery, ships, industrial furnaces, reaction towers, container racks and warehouse shelves.
H-beam

Features
High structural strength, light weight; flexible and rich design style; fast construction, small footprint, suitable for all-weather construction. It is convenient for machining, structural connection and installation, and easy to dismantle and reuse. It is a new type of steel for "green buildings". The use of H-shaped steel can effectively protect the environment. (H-Beam)
Uses
Steel structure mainly made of hot-rolled H-section steel has good plasticity and toughness, high structural stability, and strong resistance to natural disasters. It is especially suitable for building structures in earthquake-prone areas; compared with concrete structures, it can increase the structural use area ; Compared with welding H-shaped steel, it can obviously save labor and materials, low residual stress, good appearance and surface quality.
Rails
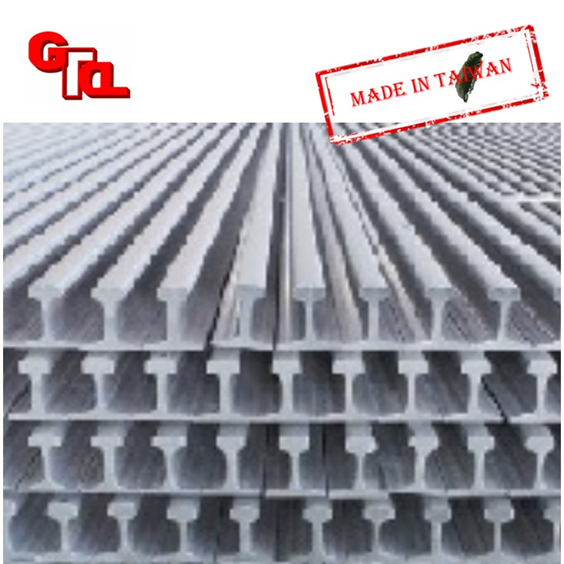
Features
The cross-section of the rail is in the shape of ``I''. When the I-shaped rail was originally designed, it was mainly hoped that when the rail head was worn out, the rail could be reused by just turning it upside down, but it was later discovered that the rail head was worn out At that time, the bottom of the rail has also been damaged due to frequent friction with the sleepers. Later, the rail has been continuously improved and still retains the I-shaped section design, mainly because the I-shaped section can withstand heavy pressure. (Rails)
Uses
Because the rails have the characteristics of thermal expansion and contraction, a certain gap must be maintained when the rails are connected (to prevent the rails from being pushed and deformed due to thermal expansion and elongation when the temperature rises), and then the rails are connected to each other with fish plates and screws Link up. The gap between the railroad tracks for thermal expansion and contraction is the source of a series of rhythmic sounds that we often hear when taking a train. However, such a design will cause the wheels to hit the rail, increase the amount of noise and vibration, reduce passenger comfort... and many other negative effects.
Single and bilateral punching angle steel
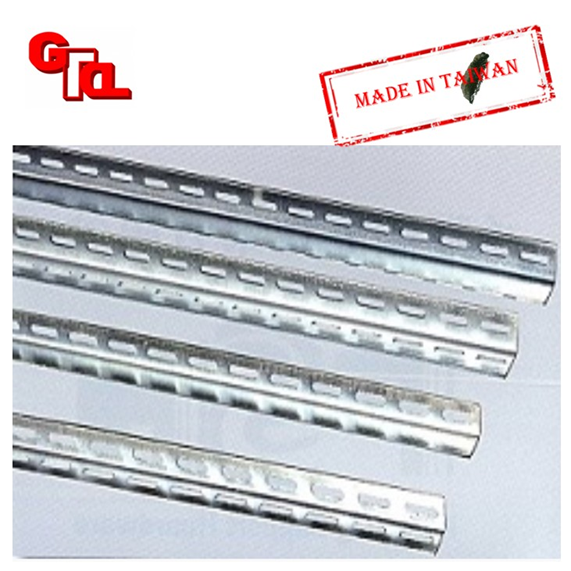

Features
Single and bilateral punching angle steel
Uses
Universal angle steel-the most commonly used shelf. Economical. Durable. Trucks. Freezers. Ladder suitable for any venue
Seamless steel pipe
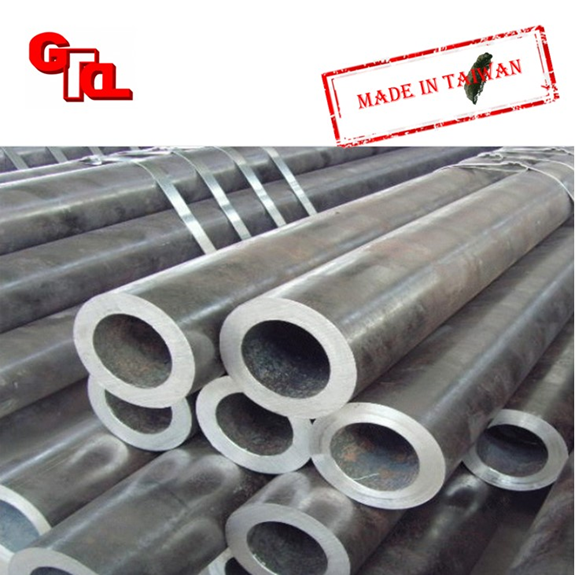

Features
JIS G3452 SGP G3454 STPG G3455 STS G3456 STPT G3460 STPL STKM13C
Uses
Seamless steel pipes for general structure, seamless steel pipes for conveying fluids, seamless steel pipes for medium and low pressure boilers, seamless steel pipes for high-pressure boilers...; according to material: high-quality carbon structural steel seamless steel pipes, low Alloy structural steel seamless steel pipe, alloy steel seamless steel pipe.
Steel for general construction
SS400




